new Label
A Label draws viewport-aligned text positioned in the 3D scene. This constructor should not be used directly, instead create labels by calling LabelCollection#add.
Demo:
See:
Source:
Methods
-
computeScreenSpacePosition
-
Computes the screen-space position of the label's origin, taking into account eye and pixel offsets. The screen space origin is the bottom, left corner of the canvas;
xincreases from left to right, andyincreases from bottom to top.Parameters:
Name Type Description contextContext The context. frameStateFrameState The same state object passed to LabelCollection#update. Throws:
-
DeveloperError : context is required.
-
DeveloperError : frameState is required.
Returns:
Cartesian2 The screen-space position of the label.Example
console.log(l.computeScreenSpacePosition(scene.getContext(), scene.getFrameState()).toString());
-
-
equals
-
Determines if this label equals another label. Labels are equal if all their properties are equal. Labels in different collections can be equal.
Parameters:
Name Type Description otherLabel The label to compare for equality. Returns:
Booleantrueif the labels are equal; otherwise,false. -
getEyeOffset
-
Returns the 3D Cartesian offset applied to this label in eye coordinates.
Returns:
Cartesian3 The 3D Cartesian offset applied to this label in eye coordinates.See:
-
getFillColor
-
Gets the fill color of this label.
-
getFont
-
Gets the font used to draw this label. Fonts are specified using the same syntax as the CSS 'font' property.
-
getHorizontalOrigin
-
Returns the horizontal origin of this label.
Returns:
HorizontalOrigin The horizontal origin of this label. -
getOutlineColor
-
Gets the outline color of this label.
-
getOutlineWidth
-
Gets the outline width of this label.
-
getPixelOffset
-
Returns the pixel offset from the origin of this label.
Returns:
Cartesian2 The pixel offset of this label.See:
-
getPosition
-
Returns the Cartesian position of this label.
Returns:
Cartesian3 The Cartesian position of this label.See:
-
getScale
-
Returns the uniform scale that is multiplied with the label's size in pixels.
Returns:
Number The scale used to size the label.See:
-
getShow
-
Returns true if this label will be shown. Call Label#setShow to hide or show a label, instead of removing it and re-adding it to the collection.
Returns:
Booleantrueif this label will be shown; otherwise,false.See:
-
getStyle
-
Gets the style of this label.
See:
-
getText
-
Gets the text of this label.
See:
-
getVerticalOrigin
-
Returns the vertical origin of this label.
Returns:
VerticalOrigin The vertical origin of this label. -
isDestroyed
-
Returns true if this object was destroyed; otherwise, false.
If this object was destroyed, it should not be used; calling any function other thanisDestroyedwill result in a DeveloperError exception.Returns:
Boolean True if this object was destroyed; otherwise, false. -
setEyeOffset
-
Sets the 3D Cartesian offset applied to this label in eye coordinates. Eye coordinates is a left-handed coordinate system, where
xpoints towards the viewer's right,ypoints up, andzpoints into the screen. Eye coordinates use the same scale as world and model coordinates, which is typically meters.
An eye offset is commonly used to arrange multiple label or objects at the same position, e.g., to arrange a label above its corresponding 3D model.
valuecan be either a Cartesian3 or an object literal withx,y, andzproperties. A copy ofvalueis made, so changing it after callingsetEyeOffsetdoes not affect the label's eye offset; an explicit call tosetEyeOffsetis required.
Below, the label is positioned at the center of the Earth but an eye offset makes it always appear on top of the Earth regardless of the viewer's or Earth's orientation.
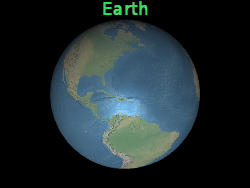

l.setEyeOffset({ x : 0.0, y : 8000000.0, z : 0.0 });
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian3 The 3D Cartesian offset in eye coordinates. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.See:
-
setFillColor
-
Sets the fill color of this label.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueColor The fill color. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setFont
-
Sets the font used to draw this label. Fonts are specified using the same syntax as the CSS 'font' property.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueString The font. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setHorizontalOrigin
-
Sets the horizontal origin of this label, which determines if the label is drawn to the left, center, or right of its position.

Parameters:
Name Type Description valueHorizontalOrigin The horizontal origin. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Use a top, right origin l.setHorizontalOrigin(HorizontalOrigin.RIGHT); l.setVerticalOrigin(VerticalOrigin.TOP);
-
setOutlineColor
-
Sets the outline color of this label.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueColor The fill color. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setOutlineWidth
-
Sets the outline width of this label.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueNumber The outline width. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setPixelOffset
-
Sets the pixel offset in screen space from the origin of this label. This is commonly used to align multiple labels and billboards at the same position, e.g., an image and text. The screen space origin is the bottom, left corner of the canvas;
xincreases from left to right, andyincreases from bottom to top.
valuecan be either a Cartesian2 or an object literal withxandyproperties. A copy ofvalueis made, so changing it after callingsetPixelOffsetdoes not affect the label's pixel offset; an explicit call tosetPixelOffsetis required.
The label's origin is indicated by the yellow point.default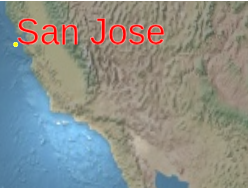
l.setPixelOffset({ x : 25, y : -75 });
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian2 The 2D Cartesian pixel offset. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setPosition
-
Sets the Cartesian position of this label.
As shown in the examples,valuecan be either a Cartesian3 or an object literal withx,y, andzproperties. A copy ofvalueis made, so changing it after callingsetPositiondoes not affect the label's position; an explicit call tosetPositionis required.Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian3 The Cartesian position. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Example 1. Set a label's position using a Cartesian3. l.setPosition(new Cartesian3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0)); ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // Example 2. Set a label's position using an object literal. l.setPosition({ x : 1.0, y : 2.0, z : 3.0 });See:
-
setScale
-
Sets the uniform scale that is multiplied with the label's size in pixels. A scale of
1.0does not change the size of the label; a scale greater than1.0enlarges the label; a positive scale less than1.0shrinks the label.
Applying a large scale value may pixelate the label. To make text larger without pixelation, use a larger font size when calling Label#setFont instead.
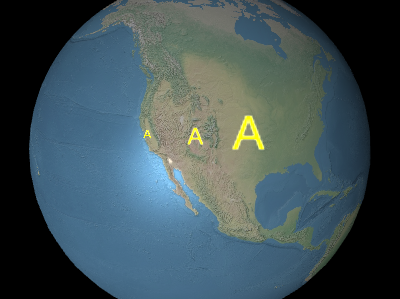
From left to right in the above image, the scales are0.5,1.0, and2.0.Parameters:
Name Type Description valueNumber The scale used to size the label. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setShow
-
Determines if this label will be shown. Call this to hide or show a label, instead of removing it and re-adding it to the collection.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueBoolean Indicates if this label will be shown. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.See:
-
setStyle
-
Sets the style of this label.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueLabelStyle The style. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setText
-
Sets the text of this label.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueString The text. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.See:
-
setVerticalOrigin
-
Sets the vertical origin of this label, which determines if the label is to the above, below, or at the center of its position.
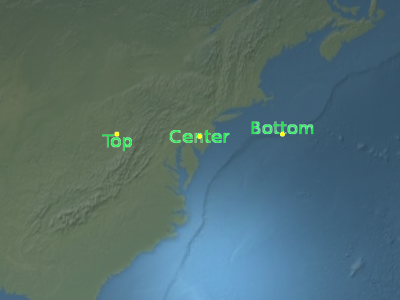
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueVerticalOrigin The vertical origin. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Use a top, right origin l.setHorizontalOrigin(HorizontalOrigin.RIGHT); l.setVerticalOrigin(VerticalOrigin.TOP);
