new Billboard
A viewport-aligned image positioned in the 3D scene, that is created
and rendered using a BillboardCollection. A billboard is created and its initial
properties are set by calling BillboardCollection#add. Any of the billboard's
properties can be changed at any time by calling the billboard's corresponding
set function, e.g., Billboard#setShow.
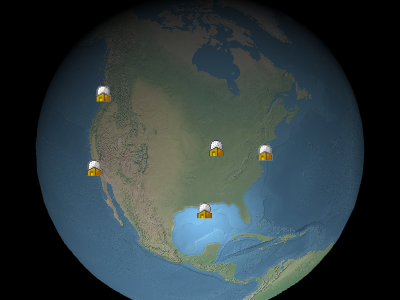
Example billboards
Performance:
Calling any get function, e.g., Billboard#getShow, is constant time.
Calling a set function, e.g., Billboard#setShow, is constant time but results in
CPU to GPU traffic when BillboardCollection#update is called. The per-billboard traffic is
the same regardless of how many properties were updated. If most billboards in a collection need to be
updated, it may be more efficient to clear the collection with BillboardCollection#removeAll
and add new billboards instead of modifying each one.
Throws:
-
DeveloperError : scaleByDistance.far must be greater than scaleByDistance.near
-
DeveloperError : translucencyByDistance.far must be greater than translucencyByDistance.near
-
DeveloperError : pixelOffsetScaleByDistance.far must be greater than pixelOffsetScaleByDistance.near
Members
-
<static> tempPixelOffset :DeveloperError
-
Computes the screen-space position of the billboard's origin, taking into account eye and pixel offsets. The screen space origin is the bottom, left corner of the canvas;
xincreases from left to right, andyincreases from bottom to top.Example
console.log(b.computeScreenSpacePosition(scene.getContext(), scene.getFrameState()).toString());
Methods
-
equals
-
Determines if this billboard equals another billboard. Billboards are equal if all their properties are equal. Billboards in different collections can be equal.
Parameters:
Name Type Description otherBillboard The billboard to compare for equality. Returns:
Booleantrueif the billboards are equal; otherwise,false. -
getAlignedAxis
-
Gets the aligned axis in world space. The aligned axis is the unit vector that the billboard up vector points towards. The default is the zero vector, which means the billboard is aligned to the screen up vector.
Returns:
Cartesian3 The aligned axis. -
getColor
-
Returns the color that is multiplied with the billboard's texture. The red, green, blue, and alpha values are indicated by the returned object's
red,green,blue, andalphaproperties, which range from0(no intensity) to1.0(full intensity).Returns:
Number The color that is multiplied with the billboard's texture.See:
-
getEyeOffset
-
Returns the 3D Cartesian offset applied to this billboard in eye coordinates.
Returns:
Cartesian3 The 3D Cartesian offset applied to this billboard in eye coordinates. -
getHeight
-
Gets the billboards custom height or undefined if the image height is used.
Returns:
Number The billboard's height or undefined. -
getHorizontalOrigin
-
Returns the horizontal origin of this billboard.
Returns:
HorizontalOrigin The horizontal origin of this billboard. -
getId
-
Returns the user-defined object returned when the billboard is picked.
Returns:
Object The user-defined object returned when the billboard is picked. -
getImageIndex
-
DOC_TBA
-
getPixelOffset
-
Returns the pixel offset from the origin of this billboard.
Returns:
Cartesian2 The pixel offset of this billboard. -
getPixelOffsetScaleByDistance
-
Returns the near and far pixel offset scaling properties of a Billboard based on the billboard's distance from the camera.
Returns:
NearFarScalar The near/far pixel offset scaling values based on camera distance to the billboard -
getPosition
-
Returns the Cartesian position of this billboard.
Returns:
Cartesian3 The Cartesian position of this billboard. -
getRotation
-
Gets the rotation angle in radians.
Returns:
Number The rotation angle in radians. -
getScale
-
Returns the uniform scale that is multiplied with the billboard's image size in pixels.
Returns:
Number The scale used to size the billboard.See:
-
getScaleByDistance
-
Returns the near and far scaling properties of a Billboard based on the billboard's distance from the camera.
Returns:
NearFarScalar The near/far scaling values based on camera distance to the billboard -
getShow
-
Returns true if this billboard will be shown. Call Billboard#setShow to hide or show a billboard, instead of removing it and re-adding it to the collection.
Returns:
Booleantrueif this billboard will be shown; otherwise,false.See:
-
getTranslucencyByDistance
-
Returns the near and far translucency properties of a Billboard based on the billboard's distance from the camera.
Returns:
NearFarScalar The near/far translucency values based on camera distance to the billboard -
getVerticalOrigin
-
Returns the vertical origin of this billboard.
Returns:
VerticalOrigin The vertical origin of this billboard. -
getWidth
-
Gets the billboards custom width or undefined if the image width is used.
Returns:
Number The billboard's width or undefined. -
setAlignedAxis
-
Sets the aligned axis in world space. The aligned axis is the unit vector that the billboard up vector points towards. The default is the zero vector, which means the billboard is aligned to the screen up vector.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian3 The aligned axis. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Example 1. // Have the billboard up vector point north billboard.setAlignedAxis(Cartesian3.UNIT_Z); // Example 2. // Have the billboard point east. billboard.setAlignedAxis(Cartesian3.UNIT_Z); billboard.setRotation(-Cesium.Math.PI_OVER_TWO); // Example 3. // Reset the aligned axis billboard.setAlignedAxis(Cartesian3.ZERO);
-
setColor
-
Sets the color that is multiplied with the billboard's texture. This has two common use cases. First, the same white texture may be used by many different billboards, each with a different color, to create colored billboards. Second, the color's alpha component can be used to make the billboard translucent as shown below. An alpha of
0.0makes the billboard transparent, and1.0makes the billboard opaque.
default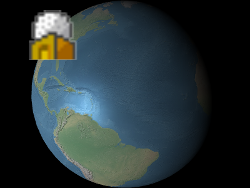
alpha : 0.5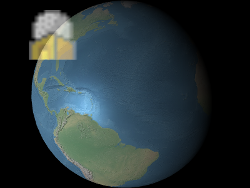
The red, green, blue, and alpha values are indicated byvalue'sred,green,blue, andalphaproperties as shown in Example 1. These components range from0.0(no intensity) to1.0(full intensity).Parameters:
Name Type Description valueObject The color's red, green, blue, and alpha components. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Example 1. Assign yellow. b.setColor({ red : 1.0, green : 1.0, blue : 0.0, alpha : 1.0 }); // Example 2. Make a billboard 50% translucent. b.setColor({ red : 1.0, green : 1.0, blue : 1.0, alpha : 0.5 });See:
-
setEyeOffset
-
Sets the 3D Cartesian offset applied to this billboard in eye coordinates. Eye coordinates is a left-handed coordinate system, where
xpoints towards the viewer's right,ypoints up, andzpoints into the screen. Eye coordinates use the same scale as world and model coordinates, which is typically meters.
An eye offset is commonly used to arrange multiple billboards or objects at the same position, e.g., to arrange a billboard above its corresponding 3D model.
valuecan be either a Cartesian3 or an object literal withx,y, andzproperties. A copy ofvalueis made, so changing it after callingsetEyeOffsetdoes not affect the billboard's eye offset; an explicit call tosetEyeOffsetis required.
Below, the billboard is positioned at the center of the Earth but an eye offset makes it always appear on top of the Earth regardless of the viewer's or Earth's orientation.


b.setEyeOffset({ x : 0.0, y : 8000000.0, z : 0.0 });
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian3 The 3D Cartesian offset in eye coordinates. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setHeight
-
Sets a custom height for the billboard. If undefined, the image height will be used.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueNumber The height of the billboard or undefined to use the image height. -
setHorizontalOrigin
-
Sets the horizontal origin of this billboard, which determines if the billboard is to the left, center, or right of its position.
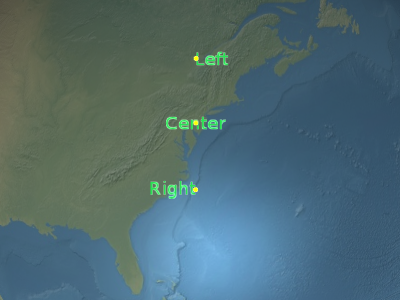
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueHorizontalOrigin The horizontal origin. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Use a bottom, left origin b.setHorizontalOrigin(HorizontalOrigin.LEFT); b.setVerticalOrigin(VerticalOrigin.BOTTOM);
-
setImageIndex
-
DOC_TBA
-
setPixelOffset
-
Sets the pixel offset in screen space from the origin of this billboard. This is commonly used to align multiple billboards and labels at the same position, e.g., an image and text. The screen space origin is the bottom, left corner of the canvas;
xincreases from left to right, andyincreases from bottom to top.
valuecan be either a Cartesian2 or an object literal withxandyproperties. A copy ofvalueis made, so changing it after callingsetPixelOffsetdoes not affect the billboard's pixel offset; an explicit call tosetPixelOffsetis required.
The billboard's origin is indicated by the yellow point.default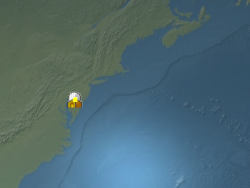
b.setPixelOffset({ x : 50, y : -25 });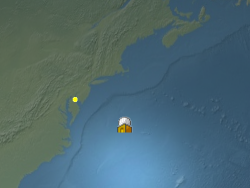
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian2 The 2D Cartesian pixel offset. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setPixelOffsetScaleByDistance
-
Sets near and far pixel offset scaling properties of a Billboard based on the billboard's distance from the camera. A billboard's pixel offset will be scaled between the NearFarScalar#nearValue and NearFarScalar#farValue while the camera distance falls within the upper and lower bounds of the specified NearFarScalar#near and NearFarScalar#far. Outside of these ranges the billboard's pixel offset scale remains clamped to the nearest bound. If undefined, pixelOffsetScaleByDistance will be disabled.
Parameters:
Name Type Description pixelOffsetScaleNearFarScalar The configuration of near and far distances and their respective pixel offset scaling values Throws:
DeveloperError : far distance must be greater than near distance.Example
// Example 1. // Set a billboard's pixel offset scale to 0.0 when the // camera is 1500 meters from the billboard and scale pixel offset to 10.0 pixels // in the y direction the camera distance approaches 8.0e6 meters. b.setPixelOffset(new Cartesian2(0.0, 1.0); b.setPixelOffsetScaleByDistance(new NearFarScalar(1.5e2, 0.0, 8.0e6, 10.0)); // Example 2. // disable pixel offset by distance b.setPixelOffsetScaleByDistance(undefined);
-
setPosition
-
Sets the Cartesian position of this billboard.
As shown in the examples,valuecan be either a Cartesian3 or an object literal withx,y, andzproperties. A copy ofvalueis made, so changing it after callingsetPositiondoes not affect the billboard's position; an explicit call tosetPositionis required.Parameters:
Name Type Description valueCartesian3 The Cartesian position. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Example 1. Set a billboard's position using a Cartesian3. b.setPosition(new Cartesian3(1.0, 2.0, 3.0)); // Example 2. Set a billboard's position using an object literal. b.setPosition({ x : 1.0, y : 2.0, z : 3.0 }); -
setRotation
-
Sets the rotation angle in radians.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueNumber The rotation angle in radians. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setScale
-
Sets the uniform scale that is multiplied with the billboard's image size in pixels. A scale of
1.0does not change the size of the billboard; a scale greater than1.0enlarges the billboard; a positive scale less than1.0shrinks the billboard.
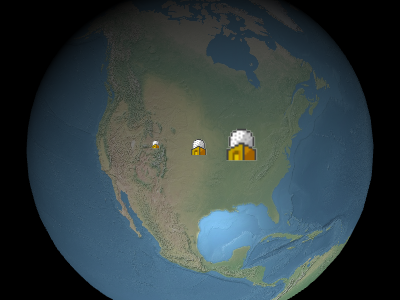
From left to right in the above image, the scales are0.5,1.0, and2.0.Parameters:
Name Type Description valueNumber The scale used to size the billboard. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required. -
setScaleByDistance
-
Sets near and far scaling properties of a Billboard based on the billboard's distance from the camera. A billboard's scale will interpolate between the NearFarScalar#nearValue and NearFarScalar#farValue while the camera distance falls within the upper and lower bounds of the specified NearFarScalar#near and NearFarScalar#far. Outside of these ranges the billboard's scale remains clamped to the nearest bound. If undefined, scaleByDistance will be disabled.
Parameters:
Name Type Description scaleNearFarScalar The configuration of near and far distances and their respective scale values Throws:
DeveloperError : far distance must be greater than near distance.Example
// Example 1. // Set a billboard's scaleByDistance to scale by 1.5 when the // camera is 1500 meters from the billboard and disappear as // the camera distance approaches 8.0e6 meters. b.setScaleByDistance(new NearFarScalar(1.5e2, 1.5, 8.0e6, 0.0)); // Example 2. // disable scaling by distance b.setScaleByDistance(undefined);
-
setShow
-
Determines if this billboard will be shown. Call this to hide or show a billboard, instead of removing it and re-adding it to the collection.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueBoolean Indicates if this billboard will be shown. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.See:
-
setTranslucencyByDistance
-
Sets near and far translucency properties of a Billboard based on the billboard's distance from the camera. A billboard's translucency will interpolate between the NearFarScalar#nearValue and NearFarScalar#farValue while the camera distance falls within the upper and lower bounds of the specified NearFarScalar#near and NearFarScalar#far. Outside of these ranges the billboard's translucency remains clamped to the nearest bound. If undefined, translucencyByDistance will be disabled.
Parameters:
Name Type Description translucencyNearFarScalar The configuration of near and far distances and their respective translucency values Throws:
DeveloperError : far distance must be greater than near distance.Example
// Example 1. // Set a billboard's translucency to 1.0 when the // camera is 1500 meters from the billboard and disappear as // the camera distance approaches 8.0e6 meters. b.setTranslucencyByDistance(new NearFarScalar(1.5e2, 1.0, 8.0e6, 0.0)); // Example 2. // disable translucency by distance b.setTranslucencyByDistance(undefined);
-
setVerticalOrigin
-
Sets the vertical origin of this billboard, which determines if the billboard is to the above, below, or at the center of its position.
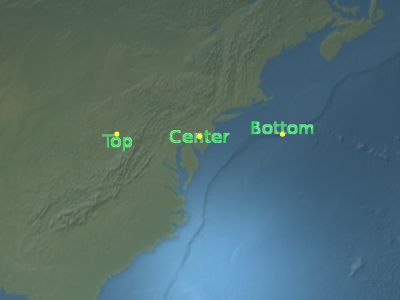
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueVerticalOrigin The vertical origin. Throws:
DeveloperError : value is required.Example
// Use a bottom, left origin b.setHorizontalOrigin(HorizontalOrigin.LEFT); b.setVerticalOrigin(VerticalOrigin.BOTTOM);
-
setWidth
-
Sets a custom width for the billboard. If undefined, the image width will be used.
Parameters:
Name Type Description valueNumber The width of the billboard or undefined to use the image width.
