Cognitive Space Enables Satellite Mission Management with CesiumJS
With eyes on NASA’s DART and Artemis missions and many of us using satellite internet or television, space is getting a lot of attention these days, from curious citizens and investors alike. Cognitive Space helps organizations fly their satellites by pairing CesiumJS with its artificial intelligence for mission management, collection planning, and communications link coordination.
Users can observe as satellites make collections in near real time, with Cognitive Space’s AI cognition engine making decisions for optimization. Courtesy Cognitive Space.
Displaying locations of imagery collection targets and ground stations and seeing how satellites point at the targets and each other require an accurate 3D globe. Cognitive Space has been using Cesium from day one for satellite constellation modeling and simulation and near real-time operations. The company got its start by serving the U.S. Air Force and Space Force before launching its commercial platform, CNTIENT, in early 2022.
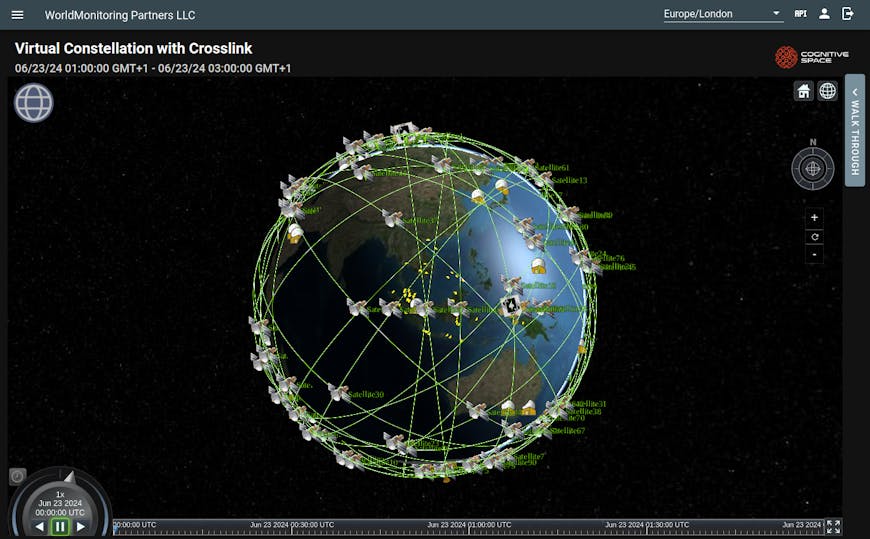
Cognitive Space has been using Cesium from day one for satellite constellation modeling and simulation and near real-time operations. Courtesy Cognitive Space.
In Cognitive Space’s CNTIENT platform, users create a study to show different planes, inclination, and altitude in 3D in CesiumJS—piquing investors’ interests or automating vital but time-consuming operations. Users can observe as satellites make collections in near real time, with Cognitive Space’s AI cognition engine making decisions for optimization. 3D replay in CesiumJS allows Cognitive Space to show its customers when collection occurred and even display why it didn’t: collecting a higher-reward target instead or full memory, for example.
Cognitive Space uses a single CZML file for the time-dynamic portions of its studies in CesiumJS. It also displays Billboard assets, polylines, points, two-line element sets from Space Track, and Bing Maps Aerial imagery from Cesium ion. (The Bing Maps dataset is saved as a local cache because of sensitive satellite info and top secret environments.) The team at Cognitive Space generates the collection targets in a custom JSON format they created. And, of course, there’s the AI: data from the company’s cognition engine includes ground station locations, space-based relay, weather, customer info on orbital configurations, and more.
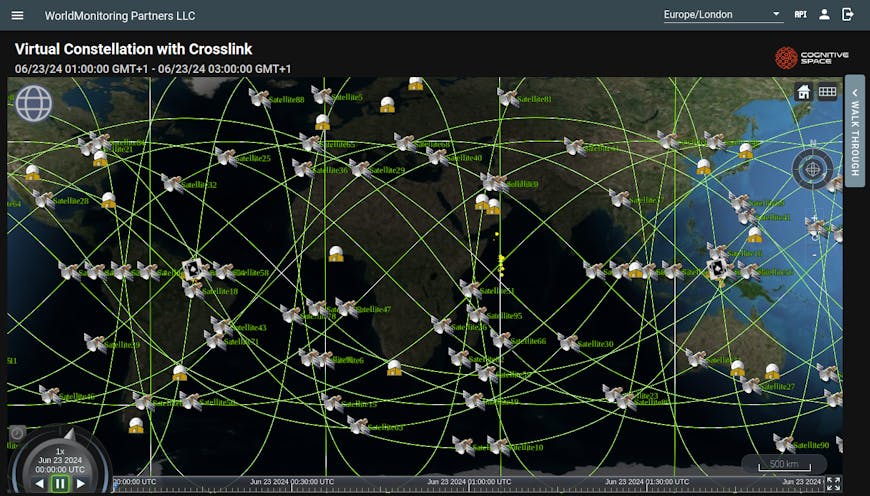
CNTIENT enables launch schedule scenarios, collection planning, and day-to-day operations for organizations of varying sizes. Courtesy Cognitive Space.
CNTIENT’s products include Forecast, which features business model, launch schedule, and orbit-selection scenarios, highlighting opportunities for future constellations; Optimize, which supports existing companies with dynamic mission planning, collection planning, and day-to-day autonomous operations in near real time; and Orchestrate, which coordinates multiple constellations and phenomenologies, primarily for government customers. All three rely on Cesium.
Because CesiumJS is open source, Cognitive Space’s developers are able to walk through the code to confirm simulations are working as expected, amend them if they’re not, and customize them for individual instances.
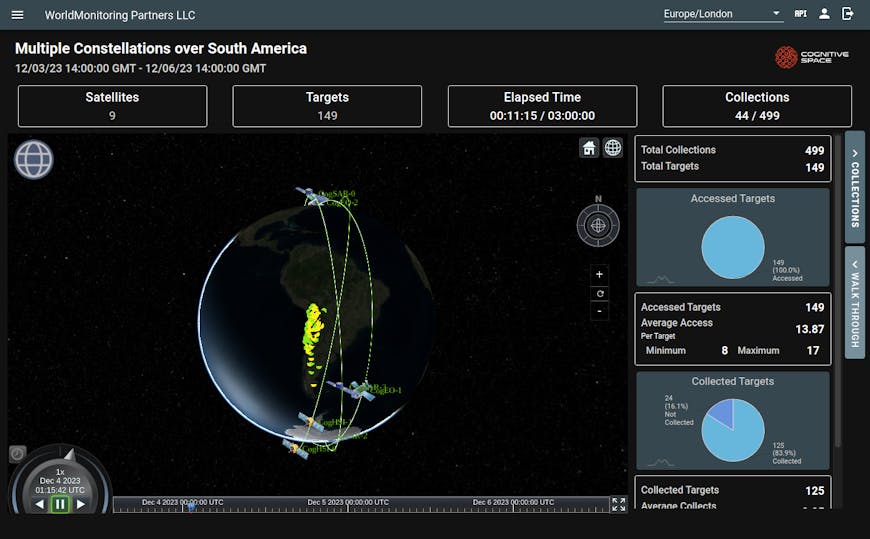
Displaying locations of imagery collection targets and ground stations and seeing how satellites point at the targets and each other require an accurate 3D globe. Courtesy Cognitive Space.
Space is hard; precision is paramount. Check out how aerospace companies are rendering massive datasets and tracking objects.