new LabelCollection
A renderable collection of labels. Labels are viewport-aligned text positioned in the 3D scene.
Each label can have a different font, color, scale, etc.
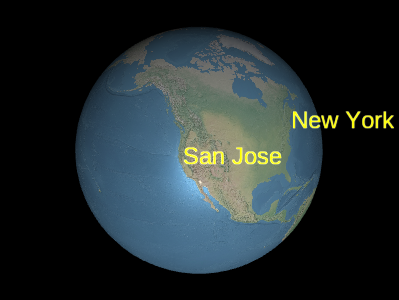
Example labels
Labels are added and removed from the collection using LabelCollection#add and LabelCollection#remove.
Performance:
For best performance, prefer a few collections, each with many labels, to many collections with only a few labels each. Avoid having collections where some labels change every frame and others do not; instead, create one or more collections for static labels, and one or more collections for dynamic labels.
Example
// Create a label collection with two labels
var labels = new LabelCollection();
labels.add({
position : { x : 1.0, y : 2.0, z : 3.0 },
text : 'A label'
});
labels.add({
position : { x : 4.0, y : 5.0, z : 6.0 },
text : 'Another label'
});
Members
-
modelMatrix :Matrix4
-
The 4x4 transformation matrix that transforms each label in this collection from model to world coordinates. When this is the identity matrix, the labels are drawn in world coordinates, i.e., Earth's WGS84 coordinates. Local reference frames can be used by providing a different transformation matrix, like that returned by Transforms.eastNorthUpToFixedFrame. This matrix is available to GLSL vertex and fragment shaders via czm_model and derived uniforms.
Example
var center = ellipsoid.cartographicToCartesian(Cartographic.fromDegrees(-75.59777, 40.03883)); labels.modelMatrix = Transforms.eastNorthUpToFixedFrame(center); labels.add({ position : new Cartesian3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), text : 'Center' }); labels.add({ position : new Cartesian3(1000000.0, 0.0, 0.0), text : 'East' }); labels.add({ position : new Cartesian3(0.0, 1000000.0, 0.0), text : 'North' }); labels.add({ position : new Cartesian3(0.0, 0.0, 1000000.0), text : 'Up' });- Default Value:
See:
Methods
-
add
-
Creates and adds a label with the specified initial properties to the collection. The added label is returned so it can be modified or removed from the collection later.
Performance:
Calling
addis expected constant time. However, when LabelCollection#update is called, the collection's vertex buffer is rewritten; this operations isO(n)and also incurs CPU to GPU overhead. For best performance, add as many billboards as possible before callingupdate.Parameters:
Name Type Argument Description descriptionObject <optional>
A template describing the label's properties as shown in Example 1. Throws:
DeveloperError : This object was destroyed, i.e., destroy() was called.Returns:
Label The label that was added to the collection.Example
// Example 1: Add a label, specifying all the default values. var l = labels.add({ show : true, position : Cartesian3.ZERO, text : '', font : '30px sans-serif', fillColor : 'white', outlineColor : 'white', style : LabelStyle.FILL, pixelOffset : Cartesian2.ZERO, eyeOffset : Cartesian3.ZERO, horizontalOrigin : HorizontalOrigin.LEFT, verticalOrigin : VerticalOrigin.BOTTOM, scale : 1.0, }); // Example 2: Specify only the label's cartographic position, // text, and font. var l = labels.add({ position : ellipsoid.cartographicToCartesian(new Cartographic(longitude, latitude, height)), text : 'Hello World', font : '24px Helvetica', });- LabelCollection#remove
- LabelCollection#removeAll
- LabelCollection#update
See:
-
contains
-
Check whether this collection contains a given label.
Parameters:
Name Type Description labelLabel The label to check for. Returns:
Boolean true if this collection contains the label, false otherwise.See:
-
destroy
-
Destroys the WebGL resources held by this object. Destroying an object allows for deterministic release of WebGL resources, instead of relying on the garbage collector to destroy this object.
Once an object is destroyed, it should not be used; calling any function other thanisDestroyedwill result in a DeveloperError exception. Therefore, assign the return value (undefined) to the object as done in the example.Throws:
DeveloperError : This object was destroyed, i.e., destroy() was called.Returns:
Example
labels = labels && labels.destroy();
-
get
-
Returns the label in the collection at the specified index. Indices are zero-based and increase as labels are added. Removing a label shifts all labels after it to the left, changing their indices. This function is commonly used with LabelCollection#getLength to iterate over all the labels in the collection.
Performance:
Expected constant time. If labels were removed from the collection and LabelCollection#update was not called, an implicit
O(n)operation is performed.Parameters:
Name Type Description indexNumber The zero-based index of the billboard. Throws:
-
DeveloperError : index is required.
-
DeveloperError : This object was destroyed, i.e., destroy() was called.
Returns:
Label The label at the specified index.Example
// Toggle the show property of every label in the collection var len = labels.getLength(); for (var i = 0; i < len; ++i) { var l = billboards.get(i); l.setShow(!l.getShow()); } -
-
getLength
-
Returns the number of labels in this collection. This is commonly used with LabelCollection#get to iterate over all the labels in the collection.
Performance:
Expected constant time. If labels were removed from the collection and LabelCollection#update was not called, an implicit
O(n)operation is performed.Throws:
DeveloperError : This object was destroyed, i.e., destroy() was called.Returns:
Number The number of labels in this collection.Example
// Toggle the show property of every label in the collection var len = labels.getLength(); for (var i = 0; i < len; ++i) { var l = billboards.get(i); l.setShow(!l.getShow()); }See:
-
isDestroyed
-
Returns true if this object was destroyed; otherwise, false.
If this object was destroyed, it should not be used; calling any function other thanisDestroyedwill result in a DeveloperError exception.Returns:
Boolean True if this object was destroyed; otherwise, false. -
remove
-
Removes a label from the collection. Once removed, a label is no longer usable.
Performance:
Calling
removeis expected constant time. However, when LabelCollection#update is called, the collection's vertex buffer is rewritten - anO(n)operation that also incurs CPU to GPU overhead. For best performance, remove as many labels as possible before callingupdate. If you intend to temporarily hide a label, it is usually more efficient to call Label#setShow instead of removing and re-adding the label.Parameters:
Name Type Description labelLabel The label to remove. Throws:
DeveloperError : This object was destroyed, i.e., destroy() was called.Returns:
Booleantrueif the label was removed;falseif the label was not found in the collection.Example
var l = labels.add(...); labels.remove(l); // Returns true
- LabelCollection#add
- LabelCollection#removeAll
- LabelCollection#update
- Label#setShow
See:
-
removeAll
-
Removes all labels from the collection.
Performance:
O(n). It is more efficient to remove all the labels from a collection and then add new ones than to create a new collection entirely.Throws:
DeveloperError : This object was destroyed, i.e., destroy() was called.Example
labels.add(...); labels.add(...); labels.removeAll();
- LabelCollection#add
- LabelCollection#remove
- LabelCollection#update
See:
